How to Install AWS CLI on Ubuntu
The AWS Command Line Interface (AWS CLI) is an open source tool that enables you to interact with AWS services using commands via your terminal. It provides direct access to the public APIs of AWS services.
Getting started with AWS CLI on Ubuntu (Linux) consists of the following steps:
- Prerequisites
- Installing the latest version of AWS CLI
- Configuring AWS CLI (short-term credentials)
Prerequisites
When running AWS CLI commands, the AWS CLI needs to have access to IAM credentials. It is recommended to not use your root account for this as it poses a security risk. If you use regular IAM you would be using long-term credentials which isn't recommended. AWS recommends the use of short-term credentials and this is one of the benefits provided by IAM Identity Center (I already have a post about setting this up). Using this aligns with the security best practices.
Now let's get to the good part!
Installing the latest version of AWS CLI
- To install the latest version of AWS CLI, run the following commands on your terminal to download the latest zip file:
curl "https://awscli.amazonaws.com/awscli-exe-linux-x86_64.zip" -o "awscliv2.zip"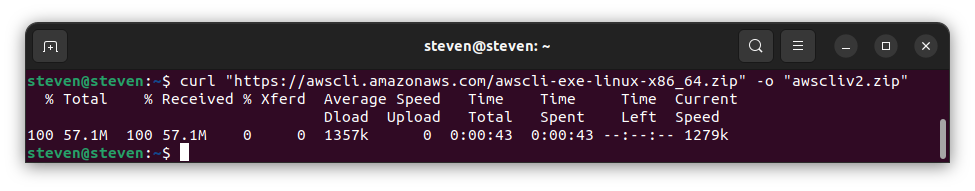
- Use the
unzipcommand to extract files from the zip file:
unzip awscliv2.zip- Use the following command to install the AWS CLI:
sudo ./aws/install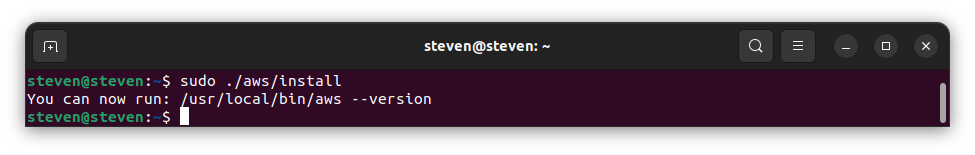
- And lastly, check the installed version using the following command:
aws --version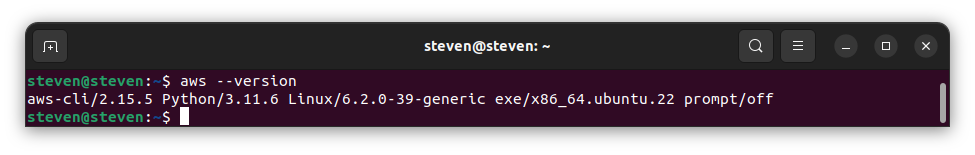
Configuring AWS CLI (short-term credentials)
Let's use the recommended short-term credentials. Here I will show you two ways in doing so:
Using AWS IAM Identity Center
Firstly, using AWS IAM Identity Center. Note that you would need to have had it enabled to use it.
aws configure sso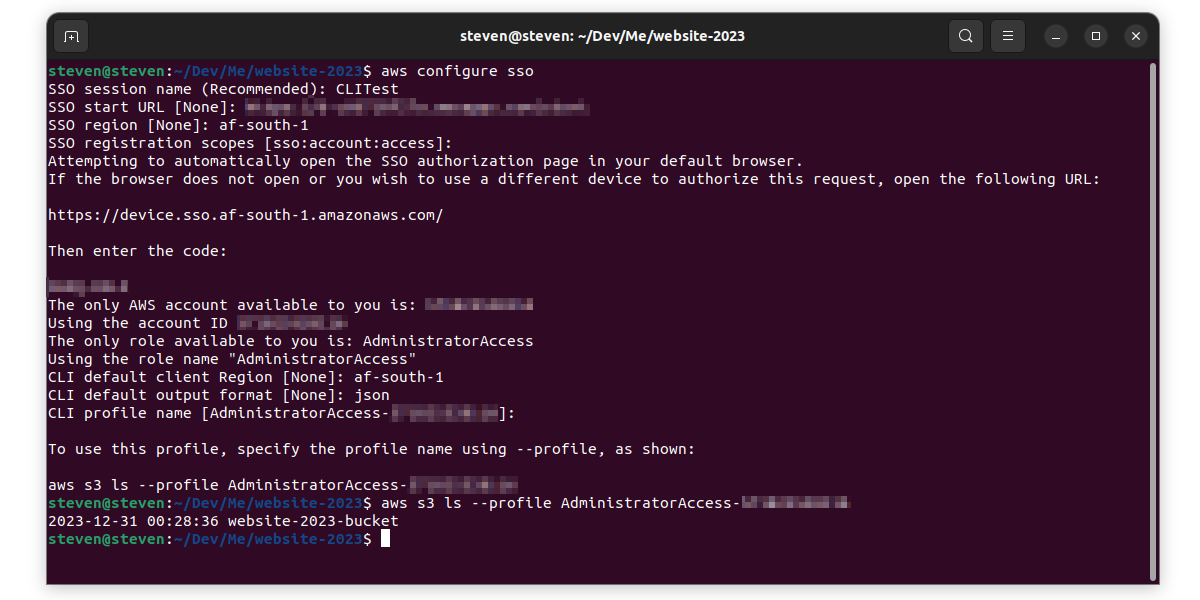
* SSO start URL [None]: https://your-app-name.awsapps.com/start
Using GetSessionToken
Secondly, Using GetSessionToken to get a set of temporary credentials. Let's say that you have configured MFA for your IAM users and want to use short-term credentials for programmatic access. GetSessionToken would return credentials consisting of:
- Access Key ID
- Secret Access Key
- Security Token
With the help of AWS Security Token Service (AWS STS), a web service that enables you to request temporary, limited-privilege credentials for users.
Running the following command:
aws sts get-session-token --serial-number arn:aws:iam::0123456789:mfa/testMFA --token-code 123456 -duration 129600Note: Replace
0123456789: with your AWS arn account IDtestMFA: with your MFA device name123456: with the MFA code currently displayed on your Authenticator app for the IAM user in question
Would return the following output:
{
"Credentials": {
"AccessKeyId": "my-access-key-id",
"SecretAccessKey": "my-secret-access-key",
"SessionToken": "my-session-token",
"Expiration": "my-expiration-date-time"
}
}- Configure your
mfaprofile:
nano .aws/credentials[mfa]
output = json
region = af-south-1
aws_access_key_id = my-access-key-id
aws_secret_access_key = my-secret-access-key
aws_session_token = my-session-token- Test and see if you're be able to list the s3 buckets within your AWS account:
aws s3 ls s3://bucket-name --profile mfaIf you want to learn more about GetSessionToken, see GetSessionToken